What is CDN?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a geographically distributed network of servers that works to speed up the delivery of internet content. Imagine a CDN like a giant storage network for websites, with outposts all over the world.
For example, think about a popular video streaming service like Netflix. When you hit play on a movie, the data for that movie isn't necessarily coming from Netflix's headquarters. Instead, a CDN might store a copy of the movie on a server closer to you. This way, the data doesn't have to travel as far, resulting in a faster and smoother playback experience.
What is Video CDN?
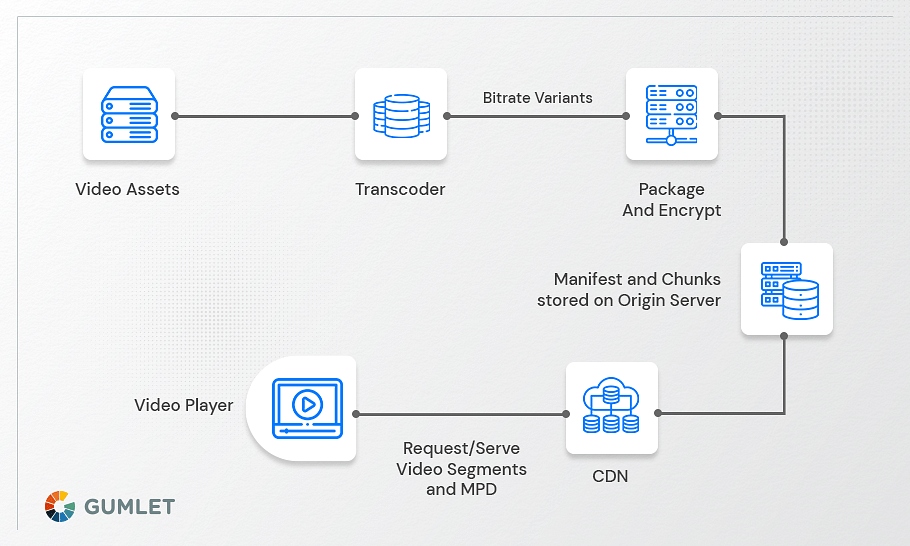
A video CDN is a content delivery network that supports video stream delivery. Its primary purpose is to speed up the delivery of video streams across the world via geographically distributed servers while simultaneously minimizing buffering time and latency, which can be tracked using latency metrics, and ensuring that the origin servers are not bombarded with non-stop requests.
A video CDN allows the origin server to share the load with corporation edge servers, rather than single-handedly fulfilling streaming requests.
Benefits of using Video CDN
- A video CDN plays an integral role in increasing streaming quality and performance by reducing budgeting, interruptions, and unnecessary lags.
- Video CDN providers allow the load to be distributed across multiple servers by creating redundancy which enhances the video streaming experience.
- In addition to reducing loading times, a video CDN lowers infrastructure costs and minimizes packet losses.
- It facilitates high scalability while ensuring latency and security.
- Since video streaming is bandwidth-intensive, it causes an inevitable overload when transmitting bulky media files via slow internet connections. With a CDN to efficiently distribute video content to different servers, it is possible to deliver high-quality streams without encountering common streaming issues.
The combination of the above-mentioned features ensures video hosting CDN provides seamless failover and safeguards your streaming platform from crashes and slowdowns.
Why Use a CDN for Video Streaming?
- Reduced latency and buffering: A CDN holds copies of your video content on servers all around the world. Viewers access the video from the nearest server, considerably lowering the distance the data must travel. This reduces latency (delay) and buffering, resulting in a smooth stream.
- Improved Reliability and Security: CDNs provide redundancy, which means that if one server fails, others may take its place. This ensures that your broadcast is live while also protecting against DDoS attacks aimed at overwhelming your origin server.
- Content Optimisation: Some CDNs have video encoding and transcoding capabilities. This enables you to provide video that is optimized for diverse devices and network connections, guaranteeing a seamless viewing experience independent of the viewer's configuration.
Top Features for Video CDN
A high-performing video content delivery network should have the following key features:
Global delivery
- Interconnected servers dispersed across strategic geographic locations ensure global content delivery.
- The American content delivery network market grew from $1.95 billion to $7.83 billion between 2014 and 2019.
Global PoPs
- CDNs support global delivery via global "PoPs" or Points of Presence.
- CDN concentrations are higher in regions with a major target audience.
HD quality network
- The closer an edge server or PoP is to the viewer, the better their streaming quality and experience.
- As the distance from the edge server, poor-quality videos, extended buffering times, low download speeds, and slow video startup times are experienced.
VOD
When choosing a video streaming CDN for your enterprise, make sure it supports key video formats, is optimized for video-on-demand (VOD) and live video platforms, and is compatible with most devices and platforms.
CDN compatibility is a characteristic of cutting-edge video transcoding, adaptive bitrate streaming, omni-device support, and adherence to streaming protocols.
Transcoding
Video content delivery systems provide accelerated distribution of large multimedia content on a wide range of web browsers, devices, players, etc.
Omni-device delivery
CDN networks ensure compatibility with different browsers, operating systems, and devices to ensure omni-device delivery.
Adaptive bitrate
Adaptive bitrate streaming allows broadcasters to deliver video content to viewers regardless of their internet connections and speeds.
Support for video formats and protocols
- Video streaming protocols and video formats facilitate content access to viewers by transferring data from one program to another.
- Compatibility with different video formats and protocols optimizes the streaming experience.
- Video formats such as MP4, MOV, FLV, CMAF, and video streaming protocols such as HLS, DASH, WebRTC, RTMP, and RTSP are widely used to enable on-demand streaming.
Video CMS
A video content management system (CMS) allows businesses to securely manage, share, and deliver video over the internet.
Content Security
Security is a key feature to look out for when choosing a CDN network for your enterprise. CDNs safeguard videos from unauthorized access and virus attacks. For example, DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) is a prominent threat online content is vulnerable to. However, using a secure CDN network, it is possible to leverage multiple safeguarding features like HTTP load balancing and encrypted traffic to prevent piracy and unwarranted attacks.
DRM
- The best CDN for video ensures internal meetings remain private.
- Role-based access control, permissions, and playback control are key features.
- CDNs integrated with DRM ensure videos are accessible only if they are granted authorization.
CDN networks like Gumlet come built-in with DRM protection to safeguard content delivery on different formats.
Best CDN for Video Streaming
Gumlet
Gumlet offers a world-class CDN network helping businesses speed up the delivery of their website content. Recognized as the "High Performer among Content Delivery Networks on G2", Gumlet is globally known to deliver faster loading times, reduce buffering times, and lower infrastructure costs.
Gumlet's geo-distributed infrastructure leverages multi-CDN rerouting to ensure 99.99% uptime for enterprises. Viewers enjoy HD quality video streaming experience and top-level security with instantly accessible video playbacks that are secured with signed URLs.
Key Features:
- Automatic format optimization for adaptive streaming.
- Real-time video manipulation capabilities.
- Built-in caching and global CDN for improved performance and scalability.
Wistia
Wistia is a video hosting and analytics platform that provides a user-friendly interface for managing, sharing, and analyzing video content.
Key Features:
- Customizable video player with branding options.
- Advanced analytics and engagement metrics for audience insights.
- Integrations with marketing tools for lead generation and conversion tracking.
Bitmovin
Bitmovin offers a comprehensive video infrastructure solution with advanced encoding, player, and analytics capabilities for seamless video streaming experiences.
Key Features:
- High-quality video encoding with support for adaptive bitrate streaming.
- Cross-platform video player SDKs for custom player development.
- Real-time analytics and performance monitoring for data-driven optimizations.
FAQs
- What are the factors to consider when choosing a Video CDN provider?
Consider factors like features, pricing, bandwidth needs, and ease of integration with your workflow when choosing a Video CDN provider.
- How much is Video CDN pricing?
Video CDN pricing varies based on features, storage, and bandwidth usage. Pay-as-you-go or tiered models are common.
- Can a Video CDN help reduce buffering and improve video quality?
Yes, a Video CDN can help reduce buffering and improve video quality by optimizing delivery and leveraging adaptive bitrate streaming.
- Can I integrate a Video CDN with my current workflow?
Yes, most Video CDNs offer embed codes or APIs for seamless integration with your website or existing workflow.