Now access to the Internet is available on almost all mobile phones, tablets, and desktop computers. Every day, millions of users, using various devices, watch the video on the Internet in real-time or in recorded form. However, in such a situation, the problem arises that different devices have different technical characteristics, bandwidth, and connection speeds. Depending on this, video files need to be created with different formats and qualities for different users.
Transcoding is a process that allows the conversion of video and audio files from one format to another, thereby creating a format suitable for the end user.
In this article, we will explore what transcoding is, its main benefits, why it is needed, and why it is crucial for video streaming. We will also learn how video transcoding works and how you can transcode your video files.
What is Transcoding?
Transcoding is the process of converting digital audio and video files from one format to another. It makes the digital content compatible with different devices, software applications, or streaming services.
Transcoding is an important step in the digital media workflow as it ensures that content can be viewed or heard on any device without compromising quality or compatibility. It also allows video and audio files to be compressed so they take up less space on storage. Transcoding also makes it possible to stream media files over the internet, as it ensures the files are in a format that is compatible with the streaming platform.
Difference Between Encoding and Transcoding
1. Encoding is the process of taking an uncompressed audio or video file and compressing it into a manageable digital format, while Transcoding is the process of taking an existing compressed digital file and converting it into a different digital format.
2. Encoding is typically used to reduce the size of an audio or video file. In contrast, Transcoding is used to maintain the same quality of an audio or video file but in a different format.
3. Encoding is usually done once, but Transcoding can be done multiple times.
Transcoding vs Transmuxing vs Transrating
Transmuxing is the process of changing the delivery format for video and audio without encoding or transcoding the original content. Transmuxing is a fairly common content delivery procedure. It differs from transcoding in that during the transcoding process some changes are made to the file after it has been unpacked.
Transrating is the process of changing the video bitrate. In this case, the video content, video format, and codec remain unchanged, and only the bit rate changes. For example, you can lower the bitrate from 8 Mbps to 4 Mbps so that the media can be streamed at a lower bandwidth. We can say that translating is a kind of transcoding.
How Does Transcoding Work?
The transcoding process includes several stages:
- Decoding the original video file into an intermediate uncompressed format.
- Conversion/scaling of the received content.
- Transcoding it into the target format.
All this can be done using special software, which is discussed in more detail below in this article.
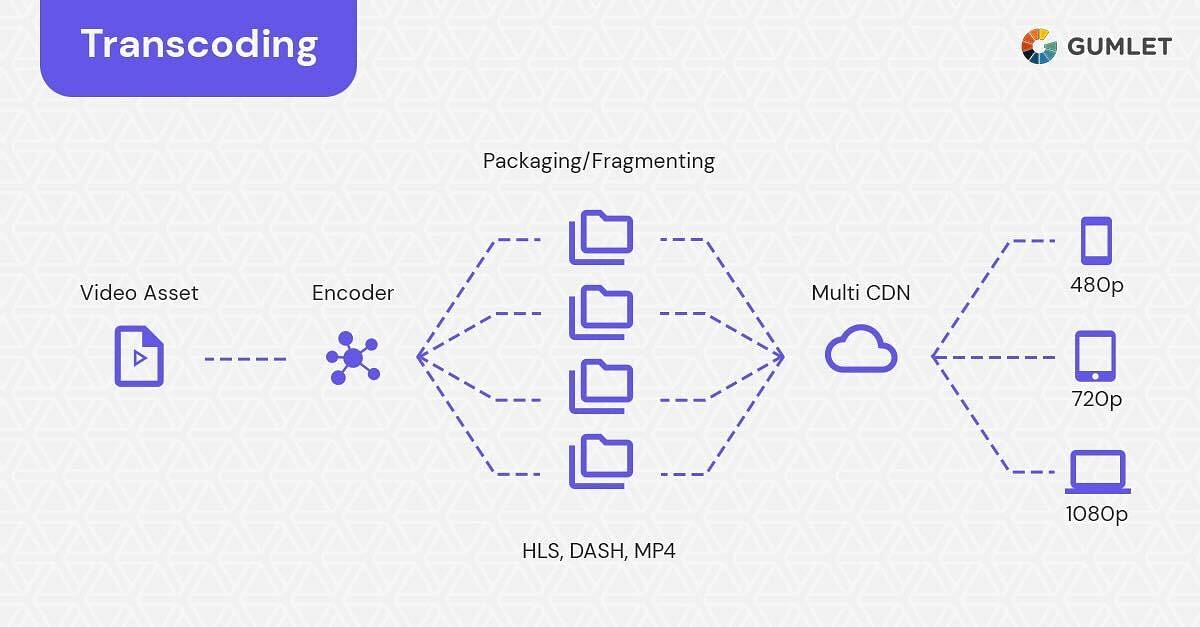
Cloud Transcoding
Cloud transcoding is where you create multiple “renditions'' of the same raw footage in the cloud. Every transcoded rendition has a different size and supports multi-bitrate streaming. An adaptive bitrate player like the HTML5 online video player optimally delivers the appropriate rendition to viewers depending on their network conditions and device capacity.
Cloud transcoding basically means the transcoding process is happening in the “Cloud” as opposed to with the help of external software.
Audio Transcoding
Audio transcoding is the conversion of an audio file to another digital audio format. While it is possible to transcode audio-only media, you can also specifically transcode the audio data of a media file that comprises both audio and video data. The process of audio transcoding largely remains the same with differences in the file formats and codecs used. For instance, MP3, FLV, WMV, AAC, etc.
Codecs and File Formats in Video Transcoding
Video transcoding works using a video codec. A video codec is a device or software that compresses video files. It removes redundant data from the file while trying to keep the file in the best possible quality. Let’s take a look at the most popular video codec types.
- HEVC/H.265 uses more efficient video compression algorithms compared to H.264/MPEG-4. It is designed in response to the growing demand for higher compression rates for moving images for a variety of applications such as Internet streaming, data transmission, video conferencing, digital storage, and broadcast television.
- VP9 is a video compression format and video codec developed by ON2 Technologies, which was acquired by Google.
A video file format is a type of file format for storing digital video data on a computer system. Video is almost always stored using lossy compression to reduce the file size. List of the most popular file formats:
- MP4 is the most widely used format. It is supported by all browsers and video players.
- QuickTime File Format is Apple's multimedia format.
- FLV. It used to be a very popular format. Its popularity has declined now as it requires a plugin to play the video, and this feature is not required for the HTML5 video component.
- WebM is an open-source Google video container format.
- Advanced Systems Format is a Microsoft video container format specially designed for video streaming.
Why is Video Transcoding Important?
Video transcoding is very important when you want your content to be available to more end-users.
Let’s take a look at the most important reasons for using transcoding.
Adaptive streaming
When you use a format such as HLS, it allows the video player to dynamically switch between video sources based on the viewer’s Internet connection and device. For example, switch between 1080p and 720p versions of the video stream.
Transcoding allows you to generate various video sources required for Adaptive Bitrate streaming(ABR) from single video input. This is great for people streaming live from environments with limited download speeds.
Transcoding also allows a stream to be transcoded into several formats, such as HLS or MPEG-DASH. This is useful when streaming to a range of devices that support different formats.
Benefits of Video Transcoding
Video transcoding is important for both the publishers and the end-users. Let’s look at the main benefits for both parties separately.
Benefits for publishers:
- Reduces the cost and complexity associated with encoding multiple resolutions and bitrate options.
- Removes playback restrictions based on codecs, protocols, and configurations available in the encoder.
- Provides the ability to use new-generation technologies.
Benefits for users:
- Lack of buffering due to low bandwidth connections.
- The ability to receive video in the format and resolution is supported by the device.
- The ability to receive high-quality video for users with the best connectivity and resolution.
Custom Transcodes for Different Directions.
Streaming to multiple platforms means the platforms would have different video input requirements. For example, Periscope recommends an input resolution of 540p. Instead of downsizing all the streams to 540p, the original video can be re-encoded to a separate, lower-resolution stream used only by Periscope.
Use-Case of Transcoding
- Transcoding is used by major streaming websites like Twitch and YouTube to make user-generated videos available in compatible formats and different qualities.
- Transcoding is widely used in film and video production to lower the resolution of camera-captured videos or to convert an edited video from one format to another for seamless delivery (e.g H.264).
- Another common use case of video transcoding is to ensure playback compatibility of live broadcasts via cameras and camcorders. For instance, it is not ideal to use an RTMP encoder and broadcast at 1080p; viewers may not have enough bandwidth and RTMP hardly enjoys widespread support for playback anymore. A transcoding software helps create optimized video streams with different bitrates and for more widely supported streaming formats like HLS to ensure playback compatibility of live streams across a variety of screens.
- Even when live streaming with an IP camera and other closed circuit systems (e.g. surveillance cameras), transcoding plays a key role in ensuring maximum reach and highest possible quality.
Drawbacks of Transcoding
- Transcoding requires significant hardware and system resources. It runs very slowly on devices with less RAM and a low-performance processor.
- Quality reduction is another very important disadvantage for lossy formats. Compression artifacts accumulate, so transcoding causes a progressive loss of quality with each successive generation, known as digital generation loss.
Why is Video Transcoding Critical for Streaming?
If a live video is broadcast without using transcoding, we can run into several problems. First, viewers without sufficient bandwidth will not be able to view the broadcast. Their players will constantly buffer. Secondly, without video transcoding and conversion, users who have devices with low connection speeds (tablets, mobile phones, and connected TV devices) will not be able to view the video broadcast.
Using a transcoder software or service, we can simultaneously create a set of time-synchronized video streams, each with a different bit rate and frame size, converting codecs and protocols to reach additional viewers. This set of streams can be packaged in several adaptive streaming formats so that they can be played on almost any device.
How Can You Transcode Your Video?
Transcoding can potentially occur via software on any PC or laptop, on a dedicated media server, or on a SaaS platform. However, it benefits from significant hardware and computer resources such as large amounts of system RAM, graphics acceleration, and high-performance processors. Transcoding HD video for editing in traditional video production (corporate video, television, etc.) can take hours even for powerful computers.
There are different types of video transcoders. They can be open-source software with a command-line interface or a program with advanced features and user interface. Also, videos can be transcoded locally or in the cloud.
Local transcoding involves using the video editing and compression software installed on the system. Cloud transcoding allows the video file to be uploaded to the cloud and set up options for the file, thus re-encoding it in different available versions.
Let’s consider the main advantages and disadvantages of both approaches local and cloud video transcoding.
Local transcoding
- Works slower.
- Creates a separate file for each version that needs to be uploaded and processed separately.
- Requires installation of video transcoding software on the system.
- No subscription fees. Pay for the software, install it, and get started with no additional fees.
Cloud transcoding
- Works quickly and conveniently. Simply upload the file to the cloud platform and select parameters for the file, and the platform will re-code it into the required number of versions.
- No need to install software as all transcoding is done in the cloud.
- A subscription fee for using the cloud infrastructure is possible.
How to Choose the Best Transcoding Service?
With the right transcoder, you can streamline your video delivery workflow and reduce costs. The key is to choose a transcoding service that best suits your workflow requirements. Here are two factors to consider:
- Cloud transcoding solution vs transcoding software: It basically depends on whether a content distributor has an on-premise infrastructure or they are hosting it in the cloud. A cloud transcoder undeniably simplifies the streaming workflow, ensures top-notch security, and promises a scalable solution that significantly speeds up processes. However, if you have a sizable private network, transcoding software may be the best way to go.
- Type of digital media you are transcoding: Transcoding is applicable to every media format, be it audio or video. While the process for transcoding might be similar, there are different file types and formats for audio and video. It is best to choose a versatile transcoding solution that is compatible with different types of media files for greater sustainability.
Gumlet offers an all-in-one, powerful transcoding solution to streamline your streaming workflow, manage media delivery, and improve playback compatibility. The one-stop transcoding video software can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, based on your workflow needs.
Conclusion
In this article, we looked at what video transcoding is and why it should be used in order to deliver video content to as many users as possible. Gumlet offers simple and convenient video transcoding. Choose the transcoder that is right for you and process your video so that it is accessible from any device in the world.
FAQs
How long does it take to transcode video?
Transcoding time depends on the tool you use. It is typically 1:1 or even faster, which means that one hour of source video file takes about one hour or less to transcode.
Does transcoding reduce quality?
Transcoding is typically used to convert raw or edited content into a format supported by the device on which it will be played. Thus, it is likely to cause a loss in quality, especially in lossy formats. However, with the right combination of codecs and bitrates, the loss of quality can be avoided. For instance, delivering video to portable devices undergoes lossless-to-lossy transcoding; however, large media files can be transcoded using lossless-to-lossless transcoding with no loss of quality.
What are some standard audio and video formats that can be transcoded?
MPEG4, 3GPP, MOV, FLV, and WEBM are among the common audio and video formats that can be transcoded.
Why do we transcode?
It makes streaming devices agnostic, provides higher-quality streams at different bitrates, and improves the streaming experience.
What is 4K transcoding?
4K transcoding refers to taking a 4K video stream as input and converting it to a lower resolution, for instance, Full HD or HD—to be streamed at, say, 4Mbps, 1Mbps, or 700 kbps. 4K transcoding requires your CPU to be at least Intel Core i7 and have a processing power of 3.2GHz and more.