What is MPEG4?
Moving Picture Experts Group-4 (MPEG4) is a versatile and extensively utilized video compression standard. It consists of a suite of video and audio compression technologies and interactive multimedia applications. MPEG4 allows for effective data compression while keeping high-quality multimedia content, making it an important foundation for various multimedia formats, including the popular MP4 container format.
Pros and Cons of MPEG-4
Here are some of the essential pros and cons of MPEG4:
Pros:
- MPEG4 offers excellent audio and video compression, reducing file sizes while maintaining reasonable quality, making it ideal for streaming and storage.
- It supports various multimedia content, including video, audio, 3D graphics, and interactive applications, making it adaptable for multiple uses.
Cons:
- The standard's versatility can lead to complex encoding and decoding processes, which may require more computational resources for playback and editing.
- MPEG4 technologies may involve patent licensing fees, potentially increasing the cost of using and implementing this standard.
What is MP4?
MP4, or MPEG-4 Part 14, is a widely used digital multimedia container format. It is intended to store audio, video, subtitles, and metadata in a single file. Because of its compatibility and efficiency, MP4 is widely used for streaming, downloading, and sharing multimedia content.
Pros and Cons of MP4
Here are some of the important pros and cons of MP4:
Pros:
- MP4 uses advanced compression techniques, delivering good video and audio quality at relatively small file sizes, ideal for online streaming.
- It allows for embedding metadata, including information about the content, subtitles, and chapter markers, enhancing the overall multimedia experience.
Cons:
- MP4 typically uses lossy compression, which can lead to some loss of quality, especially when high compression ratios are applied.
- Editing MP4 files can be more challenging compared to less compressed formats, as re-encoding can further degrade quality.
MPEG4 vs. MP4: A Comparision
| Feature | MPEG-4 | MP4 |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Multimedia container format family | Multimedia container format |
| Specification | ISO/IEC 14496 | ISO/IEC 14496-14 |
| File extensions | .mp4, .m4v, .3gp, .avi (depending on the codecs used) | .mp4 |
| Codecs | Can use various codecs like DivX, XviD, H.264, H.265 | Primarily uses H.264 and H.265 codecs |
| Compatibility | Widely supported by most devices and software | Universally supported by most devices and software |
| File size | Varies depending on the codecs used | Generally smaller than MPEG-4 files using other codecs |
| Video quality | Can range from low to high-quality | Generally good quality with H.264 and excellent quality with H.265 |
| Audio quality | Can support various audio formats like AAC, MP3, AC3 | Typically uses AAC audio format |
| Features | Can include subtitles, chapters, interactive elements | Can include subtitles, chapters, but limited interactive elements |
| Applications | Streaming media, video editing, DVD authoring, mobile devices | Streaming media, video playback, music playback, mobile devices |
Quality
MPEG4 content might vary greatly based on compression settings. MP4 is a digital multimedia container format that is noted for efficiently maintaining good video and audio quality at relatively small file sizes, making it ideal for streaming and storage. MP4 focuses on quality preservation. However, MPEG4 quality can vary due to its versatility and compression options.
Features
MPEG4 is a versatile yet complex multimedia standard that allows interactive applications, 3D graphics, and other features. MP4, on the other hand, is a subset of the MPEG4 standard that is primarily focused on storing multimedia content such as video, audio, and subtitles in a single container, providing features with improved simplicity and compatibility for media storage and playback.
Editing Capabilities
When it comes to editing features, MPEG4 generally provides greater editing options than the MP4 format. MPEG4 supports a broader range of multimedia technologies, allowing it to be used for advanced multimedia applications and editing. MP4, on the other hand, is often more limited in terms of editing and is frequently used for basic video editing and playback.
Compatibility
MPEG4 can be less universally supported, requiring specialized players or software. MP4 enjoys broader compatibility, as it's a widely recognized multimedia container format that plays smoothly on a wide range of devices, operating systems, and media players without the need for additional software or codecs.
Popularity
MP4 is more widely recognized and used than MPEG4 in terms of popularity. Because of its efficient compression and compatibility with a wide range of devices and platforms, MP4 has become a widely used multimedia container format for video and audio material.
Licensing
The key difference in licensing between MPEG4 and MP4 lies in their scope. MPEG4, as a multimedia standard, may involve patent licensing fees for the use of its various technologies and codecs, which can vary depending on the specific features employed. In contrast, MP4, being a specific container format, typically does not require patent licensing fees for its usage, making it more cost-effective for content creators and distributors.
Use Cases of MPEG4 and MP4
MPEG4 and MP4, as versatile multimedia technologies, find extensive applications across diverse domains. Let's explore prominent use cases that highlight their adaptability and impact.
Use Cases of MPEG4:
- Video Streaming: MPEG4's efficient compression and interactivity make it a go-to choice for streaming platforms, delivering high-quality content to viewers globally.
- Teleconferencing: It facilitates real-time video conferencing with excellent video and audio quality, enhancing communication and collaboration across distances.
- Digital Media Storage: MPEG4's compression capabilities reduce storage requirements, making it suitable for archiving multimedia content in various industries.
Use Cases of MP4:
- Online Video Sharing: MP4 is the preferred format for sharing videos on the internet due to its broad compatibility and good balance of quality and file size.
- Multimedia Presentations: It is commonly used for multimedia presentations, integrating video, audio, and subtitles seamlessly for educational and corporate purposes.
- Music and Podcasts: MP4's support for audio-only content, such as podcasts and music tracks, ensures a consistent user experience across different platforms and devices.
How to convert MPEG4 to MP4 and Vice Versa?
There are numerous tools available for converting between MPEG4 and MP4, including:
- CloudConvert
- Veed.io
- FreeConvert
- Convertio
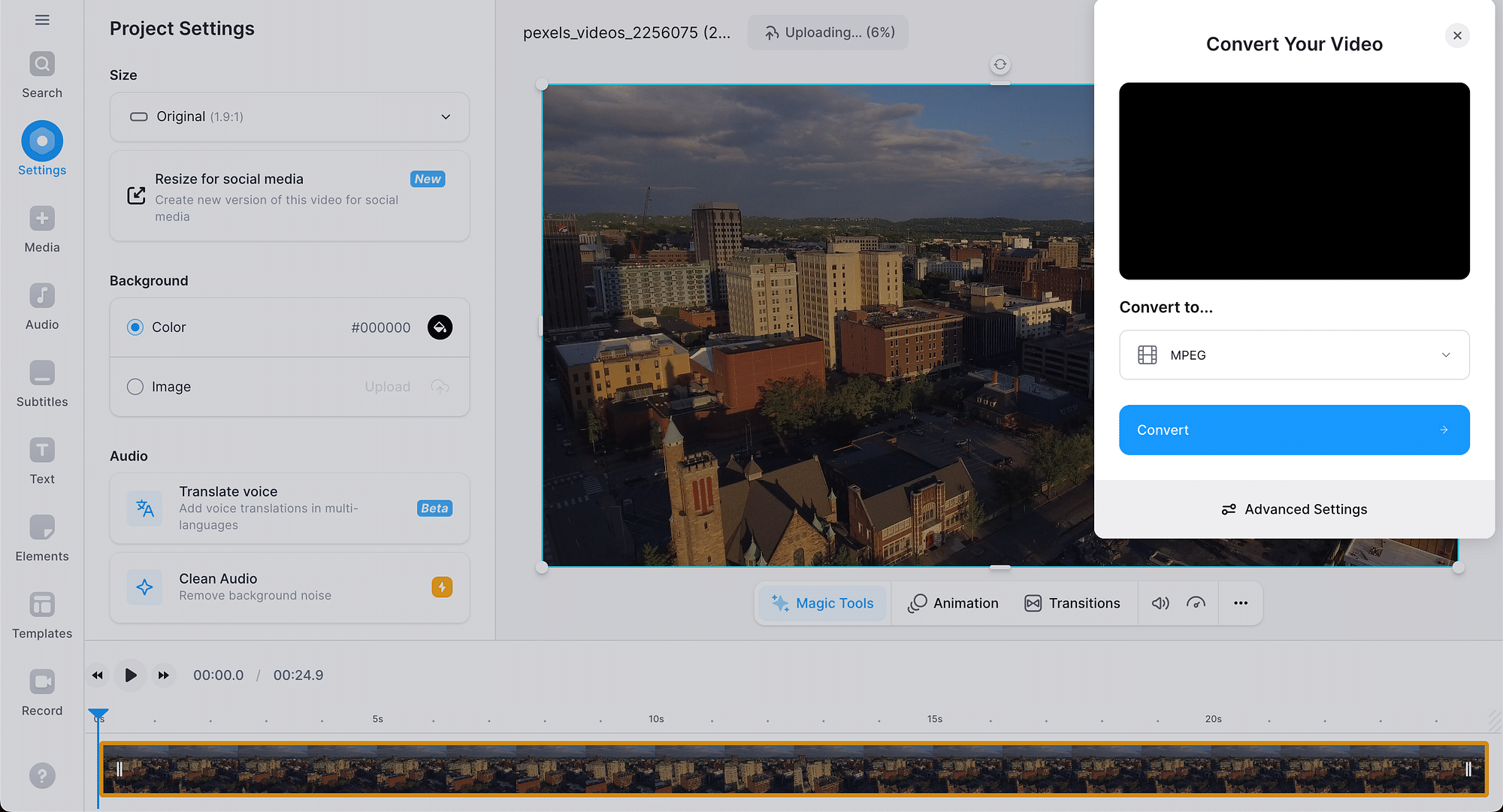
Using Veed.io as an example, here's a step-by-step guide for converting MPEG4 to MP4:
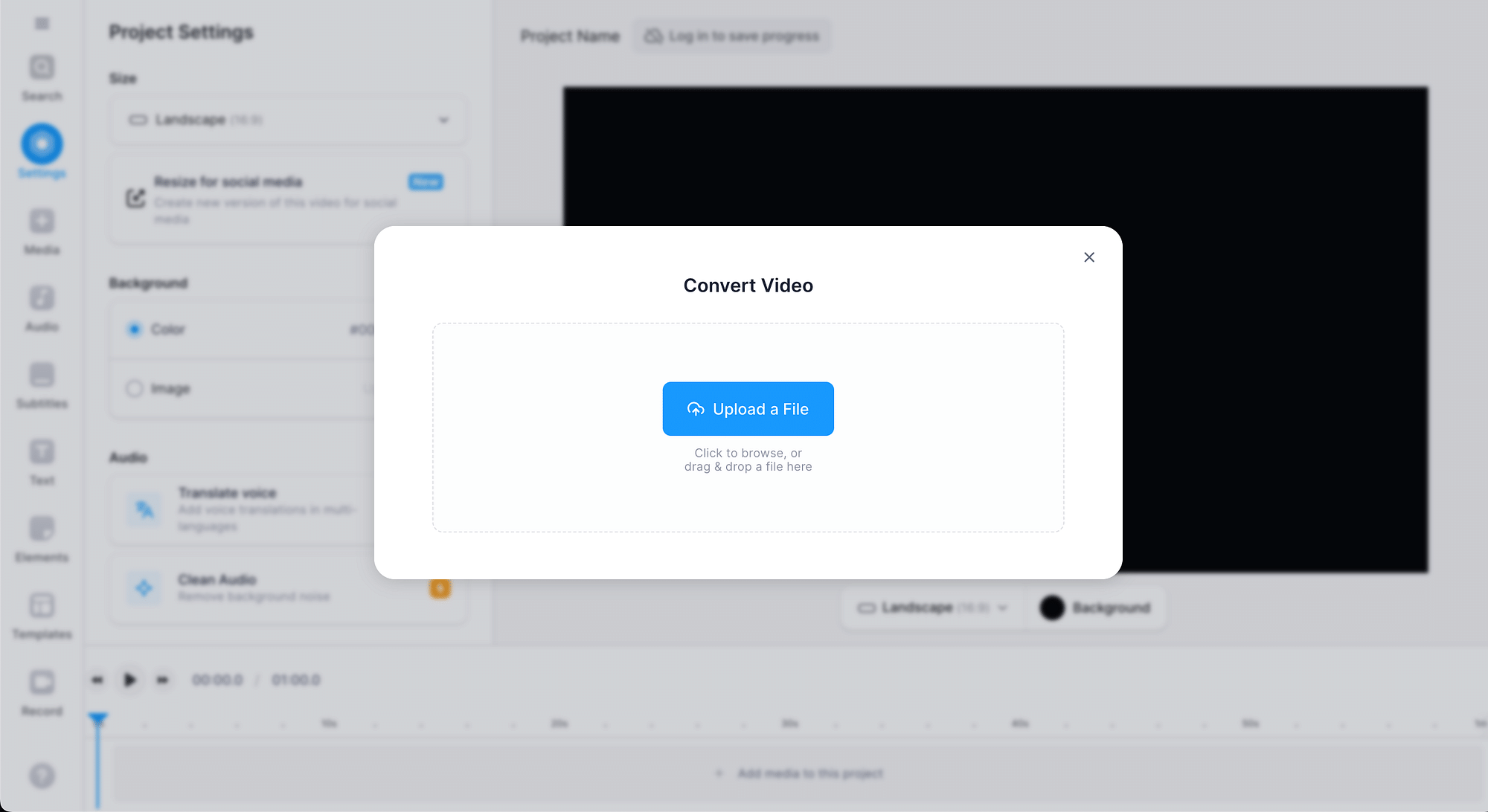
- Open the converter on the Veed.io website and upload your MPEG4 file. You can also upload a file through Dropbox or straight from a URL.
- Choose “MP4” as the output format and click on the “Convert File” button.
- Click on the “Download File” button to save your MP4 file.
- You can also edit your files to add text, auto subtitles, etc.
To convert MP4 to MPEG4, choose the MP4 to MPEG4 converter and repeat the steps.
Conclusion
Lastly, a comparison of MPEG4 and MP4 highlights their varied roles in the multimedia space. While MPEG4 is a broad standard with several applications, MP4, as a specialized container format, excels in a wide range of applications, from online video sharing to mobile entertainment. Knowing these differences helps both content providers and users to make informed decisions in the digital environment.
FAQs:
- Is MPEG4 the same as MP4?
No, MPEG-4 and MP4 are not the same. MPEG-4 is a multimedia compression standard encompassing various technologies, while MP4 is a specific digital multimedia container format used to store audio and video files. MP4 is based on the MPEG-4 standard but is a distinct format used for storage and playback.
- Is MPEG4 good for YouTube?
Yes, MPEG-4 is suitable for uploading to YouTube as it offers efficient compression while maintaining good video and audio quality, making it a common format choice for YouTube videos.
- Is MPEG4 better than MP4?
No, MPEG-4 is not inherently better than MP4. MPEG-4 is a multimedia standard, while MP4 is a specific container format within that standard. The choice between them depends on the specific use case and requirements, but for general storage and playback, MP4 is more commonly used due to its compatibility and efficiency.
- Is MP4 good for 4K?
Yes, MP4 is suitable for 4K content as it supports high-quality video and efficient compression, making it a commonly used format for 4K video playback and distribution.,