What is Cloud transcoding?
Cloud transcoding refers to the creation of multiple, different-sized “renditions” using a single video format — with the entire process taking place over the cloud. The different sizes of renditions (compressed files) employ multi-bitrate streaming to ensure a seamless streaming experience despite the strength of your internet connection.
How is it different from transcoding?
Transcoding is essentially a two-part process; it involves encoded data being decoded to an intermediary format first — and then getting encoded to the format required.
It creates multiple renditions of the same video file on the cloud so viewers can access select bit rates depending on their internet speeds to avoid prolonged buffering and slow start times.
The primary difference between cloud video transcoding and on-premise transcoding is that the latter requires a piece of hardware to complete the transcoding process whereas cloud transcoding happens on the cloud.
Whether you opt for on-premise transcoding or cloud transcoding depends on your individual business requirements, availability of resources, and budget. Cloud transcoding is typically cheaper, and requires less power, and resources.
How is cloud transcoding different from cloud encoding?
Cloud encoding and cloud transcoding are often used interchangeably; they share similar processes and are both used for converting video to streamable files. However, transcoding is different from encoding.
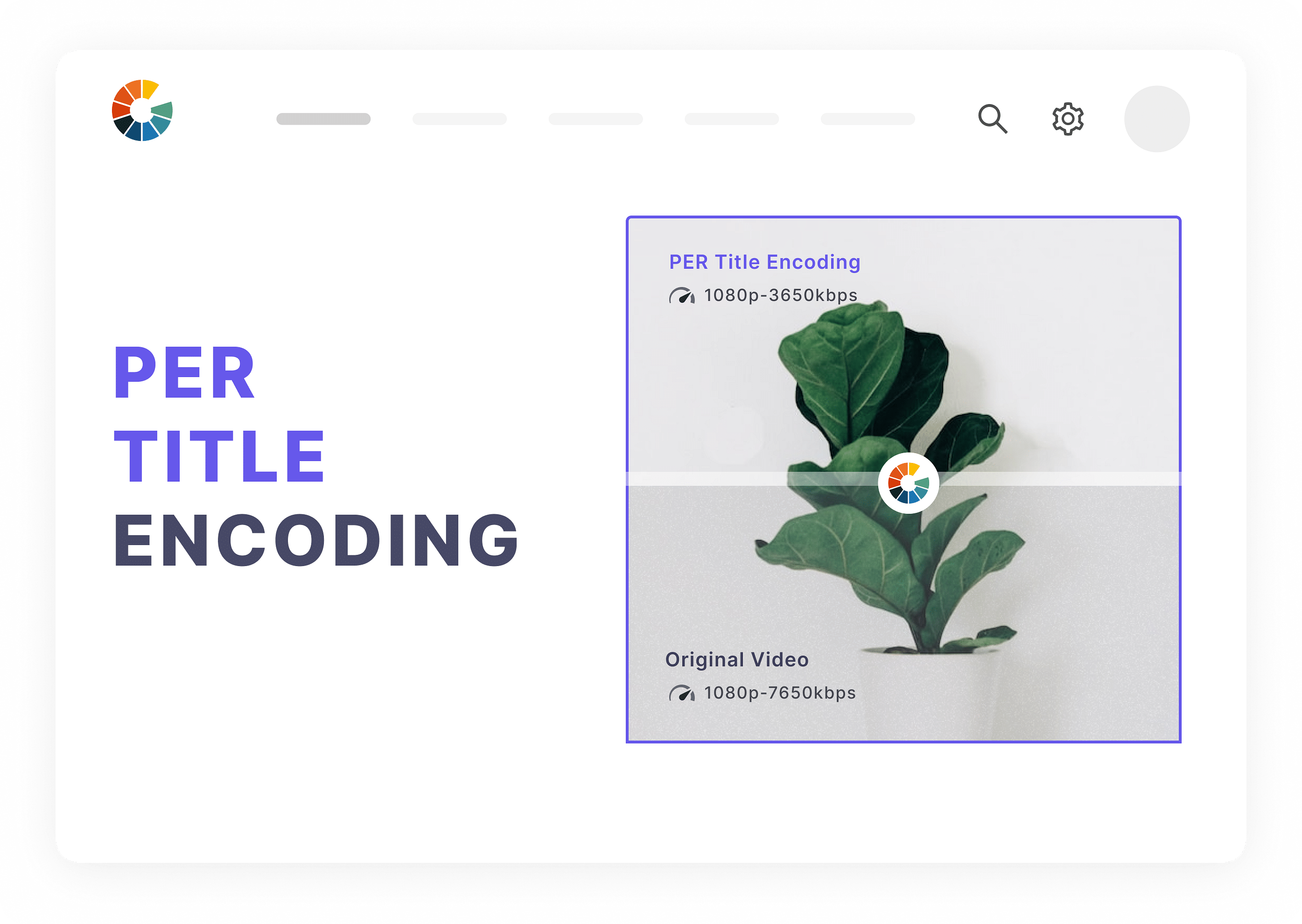
Video encoding involves the conversion of a RAW video file format to a digital format. Encoding discards unnecessary frames from a video file to reduce the overall file size and creates and transforms it into a streamable digital video file that can be streamed across a range of devices and platforms.
Transcoding, on the other hand, refers to the creation of new files from the same encoded video file, wherein each rendition has a different size, resolution, and bitrate. This ensures viewers can access different bitrates (renditions) depending on their network speed and enjoy an uninterrupted viewing experience.
To be more specific, encoding is used to change a file's format while transcoding is used to create different sizes of the same file. Encoding is typically employed in live streams but cloud-based video transcoding supports both live streaming and Video-On-Demand content.
Use Cases of Cloud Transcoding
- Transcoding is a crucial step in the adaptive streaming cycle whereby it prepares your video content for maximized output delivery regardless of fluctuating internet connections.
- For instance, a high-res, bulky video file captured using a 4K digital camera is broken down into a lower-res file to ensure ease in editing, live broadcasting, or delivering Video-On-Demand. Doing so will ensure the content is accessible by the largest number of viewers possible despite the devices they use.
- It plays an integral role in helping publishers of content, streaming services, VOD service providers, and broadcasters deliver high-quality, consistent video streams.
- Content distributors can effectively offload their transcoding requirements — be it live streaming or Video-On-Demand — to a trusted cloud-based encoding service and offset the cost of investing in on-premise hardware.
- Online video transcoding is a revolutionary technology in the field of video streaming that is helping content creators and publishers broadcast their content to the widest range of devices possible.
How to choose a video transcoding service?
Transcoding is associated with a range of benefits such as high elastic scalability and flexibility, lower capital expenditures, and overall greater streaming quality.
To ensure you get the best bang for your buck, make sure you consider the transcoding vendor's pricing model. Find out whether they charge per minute or per GB, how they charge for additional transmuxing or encoding operations (should you require it), and so on.
It is a good idea to opt for a trial run before you onboard the full-fledged system. Cloud transcoding services like Gumlet provide this option where you can get started free of cost and understand your transcoding needs as you go. Beyond that, it offers a per-minute pricing plan.
Another factor to keep in mind is the input/output formats the transcoding platform supports; H.264 and AAC codecs are the golden standards but there should also be support for HEVC, VP9, AV1, and so on.
Key benefits of using video transcoding service
Here's looking at the primary benefits a video transcoding service offers:
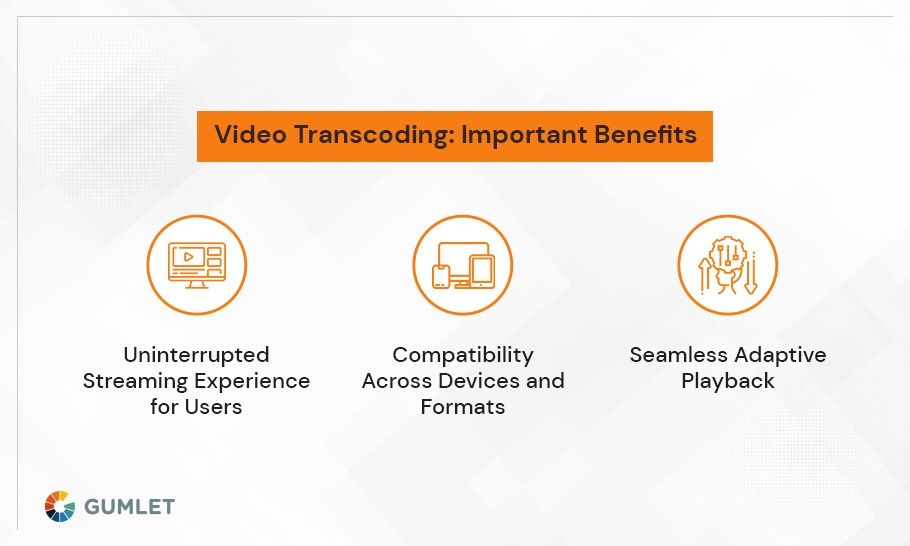
- Delivers an uninterrupted video streaming experience
Since transcoding combines several renditions of videos using an adaptive bitrate service, users can rest assured of an uninterrupted and optimized quality streaming experience despite your network conditions.
Devices running on high-speed internet connections can access top-grade video quality while those running on slow or fluctuating internet connections will receive lower-quality videos. However, any buffering issues will be eliminated with multi-bitrate streaming.
2. Ensures compatibility with a range of devices and formats
The majority of existing formats do not support streaming video content; H.264 is one of the most popular codecs and is supported by 96.96% of browsers. MP4 video codec and AAC audio codecs are other two standard file formats that are compatible with almost every device, be it a smartphone, tablet, mobile, or TV.
However, most other codecs hardly come close; they don't play the original video file as they should.
Here, cloud transcoding allows you to automatically convert AVI, MOV, MP3, and other files to the H.264 video and AAC audio codecs. Once the transcoding process is complete, it ensures all-device compatibility despite the screen size, resolution, and network conditions. Plus, there is no technical know-how required.
3. Supports adaptive playback
For users with slow internet connections, it may not always be possible to enjoy a fast and seamless real-time streaming experience. However, since cloud transcoding uses adaptive video playback to store multiple, different-sized renditions on your online video platform, you can stream video even with a poor internet connection. The video resolution will be of lower quality but issues of buffering and slow start time will almost entirely be eliminated.
There are plenty of transcoding services (free, paid, or advertising-based) that support cloud transcoding; Gumlet is one of the most reliable services to do so. It leverages effective cloud transcoding to deliver a seamless playback experience at different resolutions — 1080p, 720p, 480p, 360p, 240p.
Gumlet leverages a geo-distributed infrastructure to ensure 99.99% uptime. It provides real-time reports and almost entirely eliminates latency and re-buffering.
Transcode your video to the cloud and save time and encoding power with Gumlet today! Ensure optimum network utilization and seamless video playback at all times!
FAQs
1. What is transcoding used for?
Transcoding is commonly used to convert audio and video files into different formats compatible with different devices and platforms. It reduces the file size or bitrate, allowing it to be streamed or downloaded more efficiently.
2. Is transcoding lossless?
No, transcoding is not lossless. Transcoding involves re-encoding a video or audio file from one format to another, which can cause a loss of quality.
3. Does Netflix use transcoding?
Yes, Netflix uses transcoding for its content streaming or delivery.
4. What is a video transcoding service?
Video transcoding service makes videos compatible with different devices, archiving and creating smaller files for streaming or downloading. A transcoding service can help improve the quality of a video and make it more accessible to users.