TVOD has been around since the early days of video-on-demand (VOD) services, which began amassing popularity in the late 1990s and early 2000s. It was first introduced by pay-per-view providers, which allowed customers to order movies or sporting events in exchange for a one-time fee.
What is TVOD?
TVOD, also known as transactional video-on-demand, is a monetization model wherein customers only rent or purchase content they wish to watch rather than paying a recurring fee for the platform's entire library.
With pricing options becoming more personalized and providing greater flexibility in how customers access and pay for content, more and more providers are adopting the TVOD model to monetize their content and meet the needs of their customers. New-age technologies like virtual reality and live streaming also play a key role in bolstering the popularity and relevance of the TVOD model.
TVOD allows digital publishers to charge higher prices on high-demand, high-value content and thus has the potential to generate considerable revenue for businesses.
Examples of TVOD Platforms
Some examples of TVOD platforms include:
- Amazon Prime Video: Amazon Prime Video allows users to rent individual pieces of content for a period of time by paying a rental fee.
- Google TV: Google TV provides users access to a variety of streaming services, such as Netflix, Hulu, etc., along with the ability to purchase or rent individual movies and TV shows.
- iTunes: Offered by Apple, iTunes offers a wide selection of movies and TV shows that can be purchased for a one-time fee.
Types of TVOD Monetization Model
There are three types of TVOD monetization models:
Pay-Per-View
Pay-Per-View, or PPV, is a type of TVOD monetization model within TVOD platforms that allows users to access one-off shows or events in exchange for a one-time fee. Pay-Per-View is primarily used to monetize one-time viewable events like concerts, games, and other specific live events where users are unwilling to opt for a monthly subscription.
Electronic Sell-Through
Electronic Sell-Through is another type of TVOD, where viewers are charged a one-time fee for limitless viewability of a certain piece of content. Users can view content at their comfort and discretion rather than committing to a subscription or rental model. The ETS model is mostly used to provide access to movies and TV shows available to purchase.
Download to Rent
Download to Rent, also known as DTR, is a monetization model where a content piece is accessible for a fixed period of time for a one-time charge. It is not unlike traditional movie rental models, where viewers pay a fixed fee to rent a movie for a small period of time and then return it after the period has lapsed.
Why Choose TVOD for Your Video Streaming Business?
The primary reason why streaming businesses should use TVOD is that it allows you to derive greater value by assigning different prices to different pieces of content. Price flexibility allows businesses to attract more audiences and increases retention.
Additionally, TVOD is a highly feasible revenue distribution model for content creators that provides a precise estimation of operational costs and tenders more lucrative revenue opportunities for new VOD releases. Not to mention, TVOD is the best option for conducting one-off paid events, such as concerts or gaming matches.
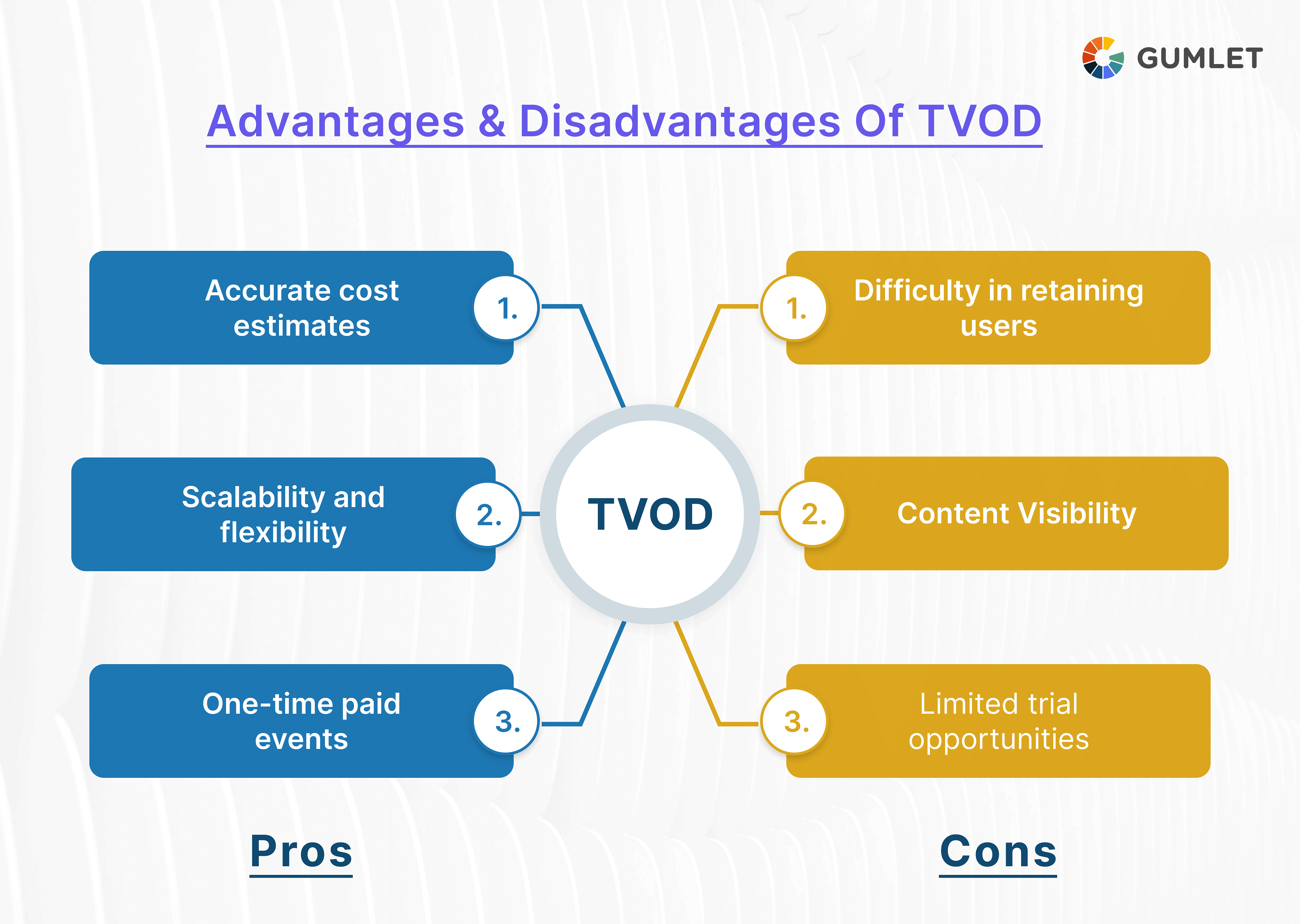
Major Advantages and Disadvantages of TVOD
Advantages:
- Accurate cost estimates: The TVOD model allows for accurate estimation of operational costs, which helps reduce the risk of unexpected expenses or bandwidth exploitation. The cost of TVOD is calculated as the cost of the server, CDN, and the amount spent to acquire a new customer.
- Straightforward revenue distribution: The revenue distribution for TVOD content is easy to track, as the user pays for specific content, thereby eliminating confusion.
- Revenue opportunities for new releases: Since new releases are usually in high demand worldwide, you can expect quick and scalable income from your audience.
- Scalability and flexibility; TVOD is best to kickstart and scale a small business. It also facilitates greater flexibility in pricing since users can either rent or permanently retain content.
- One-time paid events: TVOD is an excellent option for conducting one-time paid events, such as concerts or gaming matches.
Disadvantages:
- Difficulty in retaining users: When users pay for individual pieces, they are likely to be unmotivated to explore and purchase other content the platform publishes.
- Content visibility: TVOD is associated with challenges wrt to content recommendation; users pay for specific content, and whatever is presented to them on the homepage as a priority attracts their attention. This can limit their ability to discover other relevant content.
- Limited trial opportunities: TVOD model doesn't offer opportunities for free trials or previews. Plus, it is restrictive for bigger content sizes.
TVOD vs. SVOD: Key Differences
The primary difference between TVOD and SVOD lies in how customers pay for the content.
| TVOD | SVOD |
|---|---|
| Customers pay for each individual piece of content they wish to watch. | Customers pay a recurring subscription fee to access a library of content |
| Customers only have to pay for the specific movie or TV show they want to access. | Customers pay for the access to the entire library of content available on the platform. |
| TVOD offers customers the option to purchase content for a fixed period of time or keep it permanently | SVOD customers can cancel their subscription at any time they wish. |
| TVOD is best for monetizing exclusive, high-demand content, such as new Movies/TV shows, course certifications, live events, etc. | SVOD is particularly well-suited for streaming services which offer a wide variety of content for viewers to choose from. |
| Examples of TVOD platforms include Amazon Prime, iTunes Store, YouTube, Apple TV. | Examples of SVOD models include Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+ and Hulu. |
| TVOD model might make it challenging to retain customers as they tend to pay for specific content and go off the platform, lacking the motivation to purchase new content. | SVOD facilitates easy user retention as customers pay for the entire content library and feel motivated regularly to explore the platform and discover new content. |
Use Cases for TVOD
TVOD is majorly used in the entertainment and eLearning industries to monetize premium or exclusive content, new releases, live content, older content, and more. Here's a brief look into TVOD'S use cases:
TVOD for Online Learning
Many e-learning platforms leverage TVOD to enable instructors to create and sell courses.
- It allows them to monetize their offerings; students can pay a one-time fee to attend live classes, access specific video lessons, or acquire certifications.
- TVOD also allows course creators to offer free trials of their course, should students want to try a course before they buy.
The major companies that leverage the TVOD model for their e-learning platforms include Coursera, Udemy, Khan Academy, Skillshare, and more.
TVOD for Entertainment
TVOD is used by major streaming platforms, broadcasting networks, and high-end studios to monetize exclusive content on a pay-per-view or rental basis.
- TVOD is used to host new movie or TV season releases and other similar premium content.
- TVOD is an excellent option to monetize older TV shows and movies that are unavailable on other platforms.
- It is used for one-time live events, such as concerts, sports, and live lectures.
The companies that use TVOD for entertainment are Apple TV+, Amazon Prime Video, Google Play, YouTube, iTunes, AT&T, and more.
Why is a Video Paywall Crucial to the TVOD Model?
A video paywall is a way to restrict access to premium content by monetizing it. To put it simply, users are required to pay a one-time subscription fee or a recurring monthly charge to access content on streaming platforms.
For advertising-based monetization platforms like YouTube, where advertising revenue is the biggest income source for content creators, a video paywall offers an excellent alternative to digital publishers for generating considerable income and scaling their business.
Furthermore, the content restriction also helps prevent potential revenue loss due to piracy. Video streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime, where you have to pay a subscription fee to access their content library, are examples of video paywalls.
For video content creators looking to take their income potential into their own hands and build a business around the content they publish, video paywalls are the way to go.
A video paywall frees businesses of advertiser-driven guidelines that could otherwise interfere with their creative vision and impact the overall video output.
In a nutshell, video paywall:
- Gives you complete control over your content and income
- Protects your content from piracy and illegal distribution
- Eliminates advertising constraints from publishing
- Allows you to build a closer, more personal relationship with your viewers, and
- Prevents unnecessary third-party platform crashes
Conclusion
Finding the right monetization model for your Video on Demand platform is no cakewalk. It requires an in-depth understanding of the different options to determine how well they meet the needs and preferences of your target audience.
Suppose you're sitting on exclusive, value-driven high-demand content, such as new movie or TV season releases, course certifications, live events, etc. In that case, TVOD is the best monetization model for you. You will find that your customers willingly pay a premium when your video provides unique value.
FAQs
1. Which service pays the most: TVOD, SVOD, or AVOD?
The revenue a specific service generates is characteristic of how popular the content is, how many subscribers it has, and the pricing structure used. However, SVOD models such as Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime tend to generate maximum revenue, considering they have a massive subscriber base and charge a recurring fee. In comparison, TVOD and AVOD services may pay less since they have a smaller customer base or are dependent on advertising revenue.
2. What is the difference between TVOD and VOD?
TVOD is a transactional model that is used to monetize on-demand content. Viewers are charged a one-time amount for a certain number of views or unlimited views. VOD, on the other hand, is a general term used to refer to different video-on-demand services, such as AVOD, TVOD, SVOD, PVOD, and NVOD.
3. Is PVOD a type of TVOD?
PVOD (Premium Video on Demand) is a subcategory of the TVOD model, where customers pay a premium fee to access and watch new releases at home before they release them on other DVD platforms or streaming services.
4. What is a video monetization model?
A video monetization model refers to how a video creator or broadcaster generates revenue from their on-demand content. This can include subscription-based, advertising-based, pay-per-view, download-to-rent, and more. The primary goal of a monetization model is to compensate the creators for their premium content by making it available to users.