What is HEVC?
H.265, also known as HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding) is a video compression codec and is a successor of H.264. It is built on concepts similar to its predecessor, but it is becoming prevalent because of the rapid adoption of 4K content everywhere. Without compromising on video quality, H.265 allows video compression to happen at half the bitrate of its predecessor - H.264 - making it twice as efficient in theory. When we perform H.265 compression to the same bitrate as H.264, we find that H.265 provides significantly improved video quality. As a result of all of these benefits and upgrades, H.265 makes it easier to stream and download 4K videos - which was not possible with H.264 since it took a lot of space and had a high bitrate.
Pros and Cons of HEVC
Pros of HEVC Codec:
- HEVC supports higher resolutions, including 4K and even 8K, making it suitable for the growing demand for high-resolution content.
- HEVC offers significantly improved compression efficiency compared to H.264. It can deliver the same video quality at lower bit rates or higher video quality at the same bit rates.
Cons of HEVC Codec:
- HEVC is associated with licensing fees, which may limit its adoption in some applications.
- Older devices and software may not support HEVC natively, requiring updates or additional software to playback HEVC-encoded content.
How Does HEVC Codec Work?
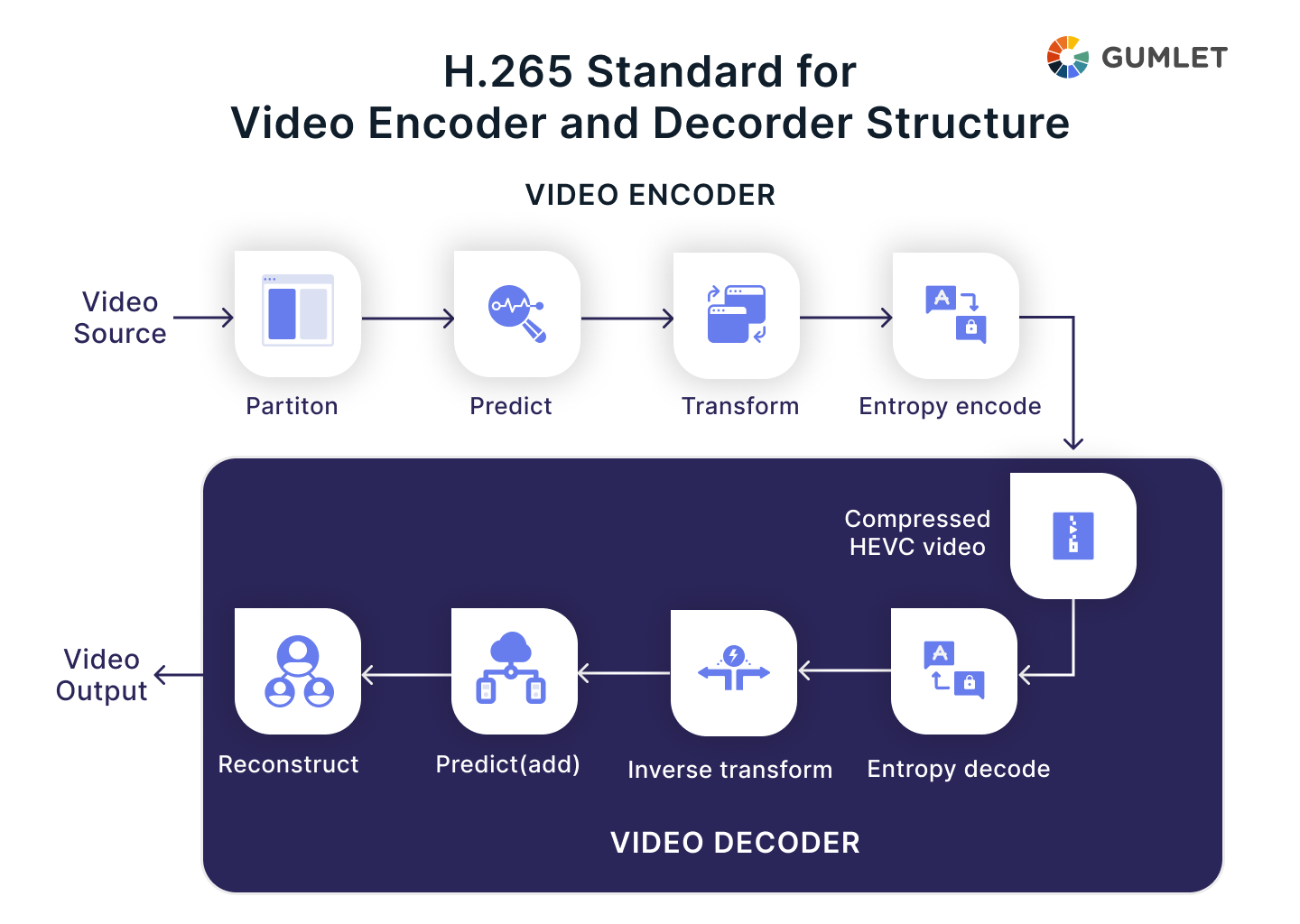
The HEVC codec is based on the same general idea and structure as the previous H.264 standard. As earlier, this has source video consisting of a series of frames which is encoded (or compressed) by an encoder, this results in a compressed bitstream. This compressed bitstream is either stored or shared, and a decoder at the other end decompresses the bitstream to create the original sequence of frames.
The HEVC codec encoder performs several steps:
- The first step includes predicting each unit and performing computations. It takes in a frame of 16x16 displayed pixels (macroblocks) and forms a prediction from the current frame or previously transmitted frames.
- The encoder then quantizes and transforms the residual, which is the difference between the prediction and the original picture unit. This is done using an approximate form of Discrete Cosine Transform, which outputs a set of coefficients relating to the weighting value of basic patterns. The initial residual is then combined to create the initial residual.
- Finally, the encoder performs entropy encoding, a lossless data compression scheme - of the transformed output, mode information, prediction information, and headers.
An HEVC decoder, on the other hand, performs the following steps:
- Entropy decoding - that is, reversing the steps performed during entropy encoding - and extracting the original elements from the sequence that was coded.
- Inverting the transformations and rescaling.
- Predicting each unit and adding it to the output of the inverse transform.
- Reconstructing the final decoded video image.
HEVC minimizes bandwidth use by identifying static areas within frames, allowing better encoding efforts. H.265, a more demanding method, uses spatial repetition within frames to reduce file size. By reducing the complexity of estimating spatial and motion resolutions, H.265 can hold back repetitive information and compress file size further. This approach allows for better application of encoding efforts in changing frames.
H.265 / HEVC Overview
The HEVC standard for video compression offers superior performance compared to H.264/AVC due to improvements such as increased partitioning flexibility, better interpolation and deblocking filters, improved signaling of modes and motion vectors, and efficient parallel processing features, making it suitable for high-end video types.
Profile, Levels, and Parameter
- Profiles are coding tools used to create relevant bitstreams.
- Encoders can choose the coding tools for a profile.
- Decoders must support all encoding tools a profile can use.
- HEVC's first version defined three profiles: Main, Main 10, and Main Still Picture.
- The second version added 21 range extension profiles, one multi-view profile, and two scalable extension profiles.
- HEVC standard defines two main tiers - High and Main, and thirteen levels.
- Levels are a set of constraints for a bitstream, with only the main tier allowed for levels below 4.
- Decoders conforming to a level/tier should decode all encoded bitstreams for that level/tier and all lower levels/tiers.
Applications of H.265
- HEVC is commonly used in video streaming platforms to deliver high-quality video content efficiently, optimizing bandwidth usage.
- HEVC is employed in television broadcasting for the transmission of ultra-high-definition content, supporting resolutions like 4K and 8K.
- HEVC is utilized in surveillance cameras and systems to enhance video compression, enabling efficient storage and transmission of high-resolution surveillance footage.
- HEVC is applied in video conferencing applications, facilitating the transmission of high-quality video with reduced bandwidth requirements for smoother online meetings.
Compare your current transcoding levels against Gumlet's advanced per-title-encoding.
Why H.265 compression?
- HEVC compression is adopted for its superior compression efficiency, enabling the delivery of high-quality video with reduced bandwidth requirements. This is crucial for streaming services, broadcasting, and video-related applications where efficient data transmission is essential.
- While browser support for HEVC has improved over time, it may vary among different browsers. Major browsers such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Apple Safari generally support HEVC, allowing a broader range of users to access HEVC-encoded content.
- HEVC is associated with patent licensing fees, which can be a barrier for smaller companies or projects with limited budgets. The licensing complexity has contributed to hesitancy in adopting HEVC in some cases.
- H.265 provides a notable reduction in file sizes while maintaining high-quality video. This space-saving feature is crucial in scenarios where storage costs are a concern, as it allows for the storage of more content within the same physical or cloud storage space.
H264 vs H265: Which is Right For You?
H264 vs H265, which is the right codec for you, let's find out:
- Compression: H.265 shines here, achieving up to 50% smaller file sizes than H.264 for the same video quality.
- Processing Power: H.265's fancy compression comes at a cost – it needs more processing power to encode and decode videos. Older devices might struggle, while newer ones might hum along just fine.
- Compatibility: H.264 reigns supreme here, supported by almost everything with a screen. H.265 is catching up, but you might encounter playback issues on older devices and platforms.
- Quality: Both deliver excellent video quality, but H.265 can maintain higher quality at lower bitrates, meaning smaller files without sacrificing visual fidelity.
Conclusion
The thing about technology is that it keeps upgrading and getting better. H.264 was undoubtedly a good compression standard, but it had some flaws. H.265 picked up on those flaws and improved on them to provide us with an even better compression standard. Rest assured that we will soon have an even more improved version of this. The goal for you, in such scenarios, should be to stay updated with all the happenings and updates so that you can make the best decision when it comes to choosing a video codec!
We hope this article gave you a good insight into the overview and workings of the H.265 compression technique!
FAQs
1. Is H.265 better than H.264?
Yes, H.265 is more efficient than H.264 in terms of compression. It can compress files to about half the size of H.264 with the same quality or maintain the same file size but at a higher quality.
2. Why is H.265 not popular?
H.265 is a relatively new video compression standard that is not widely used because it is more complex and requires more processing power than older standards like H.264. Additionally, it is less widely supported by browsers than H.264.
3. Is H.265 more CPU intensive?
Yes, H.265 is more CPU intensive than earlier video codecs like H.264. H.265 is more efficient in terms of compression, but this comes at the cost of increased computational complexity for encoding and decoding.